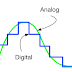
The quantities whose values vary continuously or remain,constant are know as analogue quantities.For example,the temperature of air varies continuous fashion during 24 hours of a day.If we plot a graph between time and temperature recorded at different times,we get a graph.This graph shows that temperature varies continuously with time.Therefore,we can say that temperature is an analogue quantity.Similarly,Time,pressure,distance,etc are analogue quantities.
The branch of electronics consisting of circuits which process analogue quantities is called analogue electronics.For instant,the public address system is an analogue system in which microphone converts audio or sound into a continuously varying electric potential.This potential is an analogue signal which is fed into amplifier.Amplifier is and analogue circuit which amplifies signal without changing its shape to such and extent that it can operate a loudspeaker.In this way loud sound is produced by the speaker.Radios,televisions,and telephones are few common devices that process analogue signals.
The quantities whose values vary in non-continuous manner are called digital quantities.Digital quantities are expressed in the form of digits or numbers.The branch of electronics which deals with digital quantities is called digital electronics.Digital electronics uses only two digits '0' (zero) and '1' (one) and the whole data is provided in binary form due to which processing of data becomes easy.